
A plant is a living thing that captures and uses the sun’s energy to make its food. Watch What Plants Need to Grow. Plants are the first link in a food chain. Animals and people depend on plants. The study of plants is called botany. Scientists who study plants are called botanists. Botanists divide the 350,000 kinds of plants into two groups: plants with roots, stems and leaves (such as trees, bushes, ferns, grasses, and flowers) called vascular plants and plants without roots, stems or leaves (like moss and algae) called non-vascular plants. Vascular plants are more complex than non-vascular plants which are simple. Take a look at the Integrated Taxonomic System as a way to explore types and locations of plants. Most plants live on land, but some live in and near water. Most plants begin life as seeds. Seeds have everything they need to reproduce into a plant, but they cannot grow if they are covered in fruit. Seeds are carried by people, animals, water, and the wind. When seeds are planted or land on land, they have to have enough water, good soil and sunlight, to grow. Check out NEXT.cc SEED Journey.
When seeds begin to grow, they extend roots below ground and shoots above. Shoots can grow buds, leaves, stems, flowers, fruits and vegetables. Plants can be annuals (one growing season only), perennials (many growing seasons) and biennials (two growing seasons). Through photosynthesis, plants convert energy from the sun into sugars, breath in carbon dioxide, and release oxygen. The pigment that makes a plant green, chlorophyll, is responsible for converting sunlight into glucose as useable chemical energy.
Plants clean the air we breathe, feed us, clothe us, help define our climate zones and shape the environments in which we live. Plants are an integral part of our healthy earth and our healthy life.
Plant Power!
Activity 1 – Evolution of plants

Activity 2 – You and a Beanstalk!

Find a container, some potting soil, bean seeds and organize a sunny, warm place to place your planted seeds. Keep the seeds moist and in a sunny windowsill. In a few days your bean seeds should sprout. You can even plant a lemon seed. Watch this video to how easy it is to start. How to Grow a Lemon Tree From a Lemon Seed. Record its daily progress. When the seeds are three inches tall or more turn their pot around. See what happens the next day. Do your beans act like a solar collector and follow the sun? That’s plant power! Plants have hormones that cause the cells closet to the light to grow more quickly. This is called phototropism. Remember, as your plant grows taller and bigger, it will need a bigger pot!
Let’s get started growing!
Activity 3 – Diagram a Plant

Using the links on the explore page of this journey, draw a plant. Diagram and label the parts. Start with the seed. Visit NEXT.cc’s SEED Journey to see all of the different shapes and sizes of seeds. Seed are inside the fruit of plant-hard like a nut, medium like a lemon, or soft covered like a grape. Once the seeds are planted in soil with the amount of moisture and temperature range that they need, they begin to grow roots down, up , and in some plants out. The main types of roots are Tap, Fibrous, Prop, and Adventituis. A*Tap roots* grows straight down anchoring the plant in the soil. Fibrous and Prop roots grow sideways , in vertical layers, and radially. Roots drink up the minerals and moisture form the soil to give the plant energy to grow. After seeds grow they break through the soil with a stem. Fruits grow to protect the new seeds. Leafs multiply and capture the sun’s energy to tune CO2 into glucose and to give off oxygen. And finally some plants have flowers.
Be a botanist!
Activity 4 – Plant Processes

Once you can name the parts of a plant, look at how plants take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen. Leaves of a plant take in sun and water as needed through their cells. This process is called Photosynthesis. Make a diagram that shows (and labels) the steps of photosynthesis.
Activity 5 – Plant Cells Let Light and Moisture In!

Explore Label the Cells.When you think you know the names of the parts of a plant cell, draw a cross section. A plant cell has a cell wall so it is called a eukaryotic cell. Label the main parts and list their function: nucleus, nucleolus, coaxial centrosome, centriole, golgi, lysosome, peroxisome, secretary vesicle, cell membrane, mitochondrian, vacuole, cell wall, chloroplast, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton. Become a cell analyst!
Let the light in!
Activity 6 – Plant Types
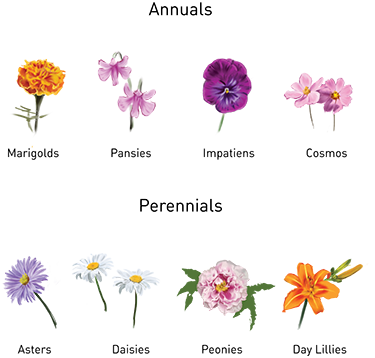
Plants that grow and come back every year are called perennials; perennials are hardy plants that can survive seasonal temperature extremes and still return in the spring. Annuals are plants like certain herbs, vegetables and flowers that only grow for one season and must be planted anew each year. Look around your yard. Which plants do you think are annuals? Which plants do you think are perennials? Make a chart of the plants at your house and at your school. Draw or photograph the plants in winter and summer seasons to show if they are dormant(sleeping) in the cold season and growing in the warm season.
seasonal: vegetation that blooms, grows or colors a garden differently during seasons perennial: plants that come back again every year annual: plants that grow only for one season
Activity 7 – Indoor Plants/Outdoor Plants

Plants can live indoors and out of doors. Outside is their native and first environment, with the sun, the rain, and the available soil. But some plants can be potted and brought inside. Plants inside benefit us as much as plants outside. Plants outside drink in Carbon Dioxide and give off Oxygen. Plants inside also improve indoor air quality. Use Nature to beautify your house inside and outside with plants. Upload a photo of an indoor plant and/or an outdoor plant and tell it thank you for cleaning the air! Plants are our friends!
Activity 8 – Plants are Used For Many Things!
Plants are used to produce many things. What plants do you wear? What plants moisturize your skin? Which plant products do we use to build homes? Which plant products are medicine? Which plant products are used in cosmetics? Look around your house or your classroom. Make a list of as many plant products as possible. Think of things you eat, wear and use and make a chart in your journal to see which plant types are used the most.
Plants clean the air we breathe, feed us, clothe us, help define our climate zones and shape the environments in which we live. Plants are an integral part of our healthy earth.
Be thankful for plants!
Review

- Wheat is one of the most important food crops in the world.
- Some plants do not have roots or stems.
- Fruits and vegetables are different parts of a plant.
- If the climate in a region changes, the plant types will still remain the same.
- Chlorophyll is responsible for:
Explore
- 4H Children's Garden, Michigan State
- Amazing Wheat!
- App Plant Net ID
- Arable Seed Identification
- ArtPlantae:Naturalists, Artists&Educators
- Ask a Biologist:Time Traveling Plants
- Botanicum A Floral Encyclopedia
- Carnivorous Plants!
- Carnivorous Plants!
- Cells Alive 3D Cells
- Chelsea Physic Garden
- Digital Botanical Illustration Niki Simpson
- Do Plants Eat? MyTE
- Ecoregions of the World
- EDC Photosynthesis Digital Game
- Fall Leaf Color
- Field Museum Guides to Plant Types
- Flower & Leaf Terminology, Artist Linda Vorobik
- Genetics Alive!
- GEO PLantNet
- Georgia O'Keefe Museum: Natural & Still Life Forms
- Georgia O'Keefe Paintings
- Gizmo Fast Plants Growth & Genetics
- Glass Flowers Harvard Natural History Museum
- Great Lakes Pollinator Plants
- Great Lakes Pollinator Plants
- Greenbug and OIT and AI to protect Nature
- Inhabitat Must Have Houseplants!
- ITSI Decomposition of Plants
- La Mannahatta
- Light and Color in Photosynthesis
- Living Walls/Vertical Garden
- Math Patterns on Plants
- Monet’s Water Lilies
- Munsell Plant Tissue Color Chart
- Munsell Soil Color Chart
- Nature Field Study Seed Dispersal
- NOVA Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis and Fossil Fuels
- Photosynthesis Smithsonian
- Plant Cell Coloring
- Plant Cell Lab
- Plant Cells Interactive (choose)
- Planting Science
- Plantiverse Plant Driven Systems
- Plant Nutrition Games
- Plant Parts Quiz
- Plant Processes PDF
- Plant Products
- Plant Relations: A First Book on Botany
- Plants Invasive
- Plants Taxonomic Information System
- Plants & The Environment
- Plant structure
- Plant Structure and Function
- Replicating Photosynthesis
- Science Snap Seed Germination
- Seed Dispersal Adaptation
- Seed Dispersal Matching
- Smithsonian Botanical Illustration
- Stephanie Nava Consider a Plot Exhibit
- TEDed How Plants Defend Themselves
- TEDed How Plants Tell Time
- The Intelligent Plant Michael Pollan
- Thomas Little Plant Whisperer UrbanGreenGardens
- USDA Plant Database
- Video Energy in Chemical Processes&Life
- Video FLowers, Seeds & The Life Cycle
- Video grow a lemon tree
- Video Photosynthesis & Food
- Video Plants & Animal Cells Khan Academy
- Video Plants & Their Seeds
- Video The Big Plant and Riveredge
Relate
- Aquaponics
- Aquifers
- Architecture
- Art Nouveau
- Biomes
- Biophilia
- Color
- Coral Reefs
- Energy
- Flowers
- Food
- Forests
- Grass
- Grasslands
- Green Roofs
- Growing food
- Land
- Landscape
- Nature
- Nature Play
- Parks
- Plants
- Pocket Parks
- Rain Gardens
- SEEDS
- Site Analysis
- Site Programming
- Soil
- Solar Energy
- Sunlight
- Topography
- Tree Identification
- Urban Agriculture
- Vegetable gardens
- Vermiculture
- Vertical Farming
- Water
- Wetlands
- Wood



















































